KurrentDB 25.1: Secondary Indexes and Multi-Stream Appends
We are excited to announce the release of KurrentDB 25.1, which marks a substantial milestone towards enhancing data accessibility and flexibility. This release introduces secondary indexes, enabling efficient querying of events by category or event type without the overhead of link resolution. Additionally, we have added support for multi-stream appends, allowing users to append events to multiple streams in a single operation, thereby reducing the need for coordinated transactions and improving performance.
KurrentDB 25.1 also includes the following new features and improvements:
- Database stats in the embedded web UI
- Preview of SQL queries
- Ability to run KurrentDB as a Windows Service
- Export logs to OpenTelemetry-compatible backends
- Apache Pulsar sink for Connectors
- Log record properties (headers)
- New metrics
Follow the Upgrade Guide for 25.1 to upgrade from EventStoreDB or earlier versions of KurrentDB to the latest version.
New features
Secondary Indexes
KurrentDB 25.0 introduces the initial release of Secondary Indexes: a new major feature that allows efficient querying of event streams based on indexed fields. The initial version supports two default secondary indexes:
- Category index: Indexes events by their category, enabling quick retrieval of all events within a specific category.
- Event type index: Indexes events by their event type, allowing for efficient querying of events of a particular type.
This feature has also enabled us to add database statistics and an SQL query preview in the embedded web UI.
Quick summary
- When first enabled (by default in v25.1), KurrentDB will start building the secondary indexes in the background.
- When fully built, the indexes can be used to efficiently query events by category or event type.
- Indexes provide a more efficient way to query events compared to system projections that create linked streams.
- Entries in secondary indexes can be removed when the original event is deleted, ensuring that indexes only contain records that can be resolved. This is not yet implemented in v25.1 but is planned for a future release.
- Secondary indexes take up to 80% less storage space compared to link events created by system projections.
Using secondary indexes
Both read and subscription operations are supported using secondary indexes. A special kind of filter is used for all operations that read from or subscribe to $all. The server interprets these filters and uses the secondary indexes to efficiently return matching events.
Refer to the documentation for more information, including usage examples, considerations, and current limitations of the feature.
Multi-stream appends
KurrentDB 25.1 introduces support for multi-stream appends, allowing users to append events to multiple streams in a single operation. This feature enhances flexibility and performance by reducing the need for coordinated transactions across multiple streams.
Multi-stream appends can be performed using the KurrentDB client libraries, which provide methods to append events to multiple streams atomically. This is particularly useful in scenarios where related events need to be recorded across different streams, such as in complex business processes or workflows. Optimistic concurrency control is supported for multi-stream appends, allowing users to specify expected versions for each stream involved in the operation.
Using the new feature requires upgrading to the latest client libraries that support multi-stream appends.
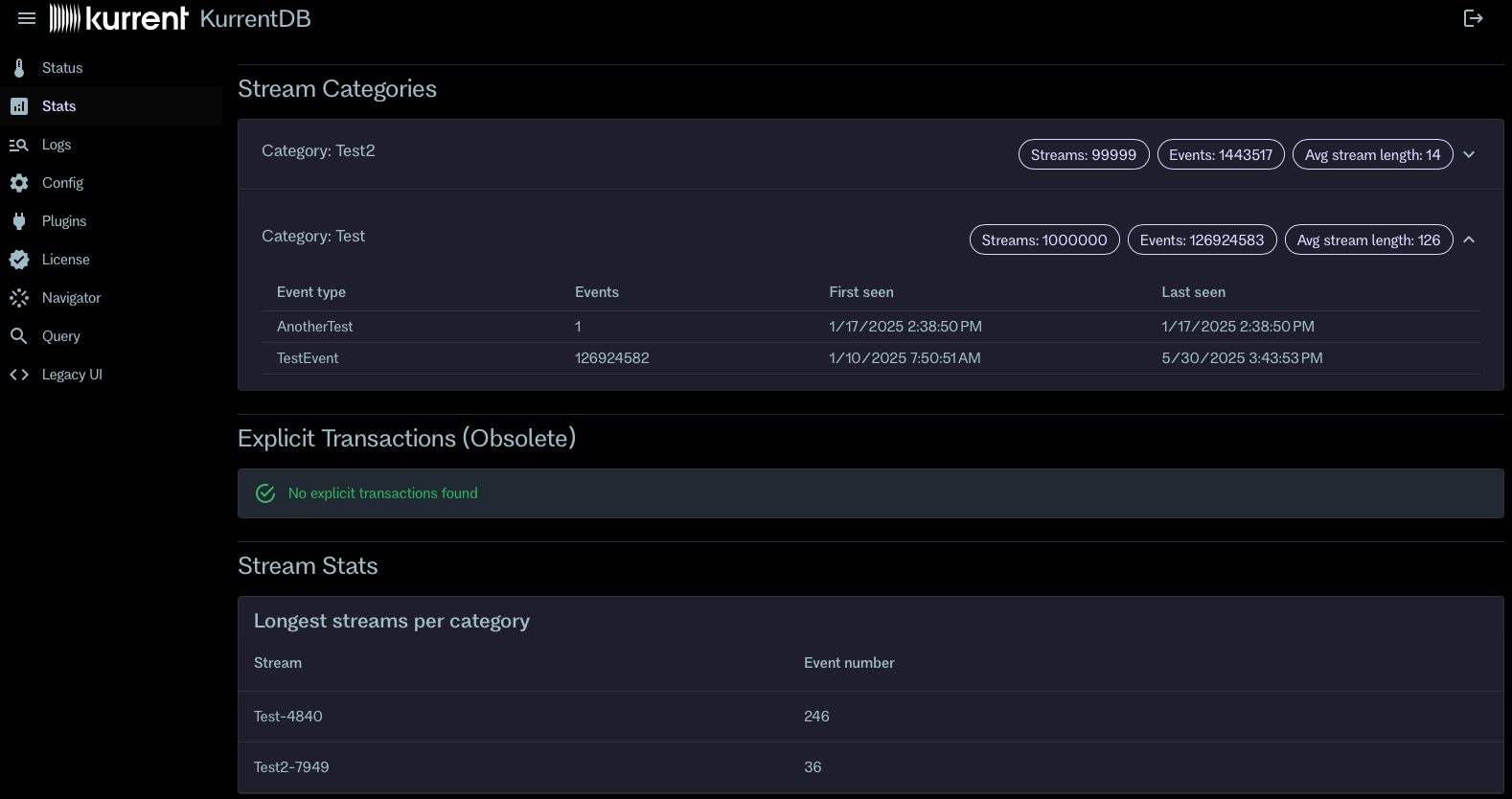
Database stats in the embedded web UI
KurrentDB 25.1 adds a new “Stats” page in the embedded web UI, providing users with insights into the database’s content. The Stats page displays various statistics, including:
- Total number of streams
- Total number of events
- List of categories and event types with their respective event counts
- Number of streams per category
- Longest streams
- Presence of explicit transactions in the database
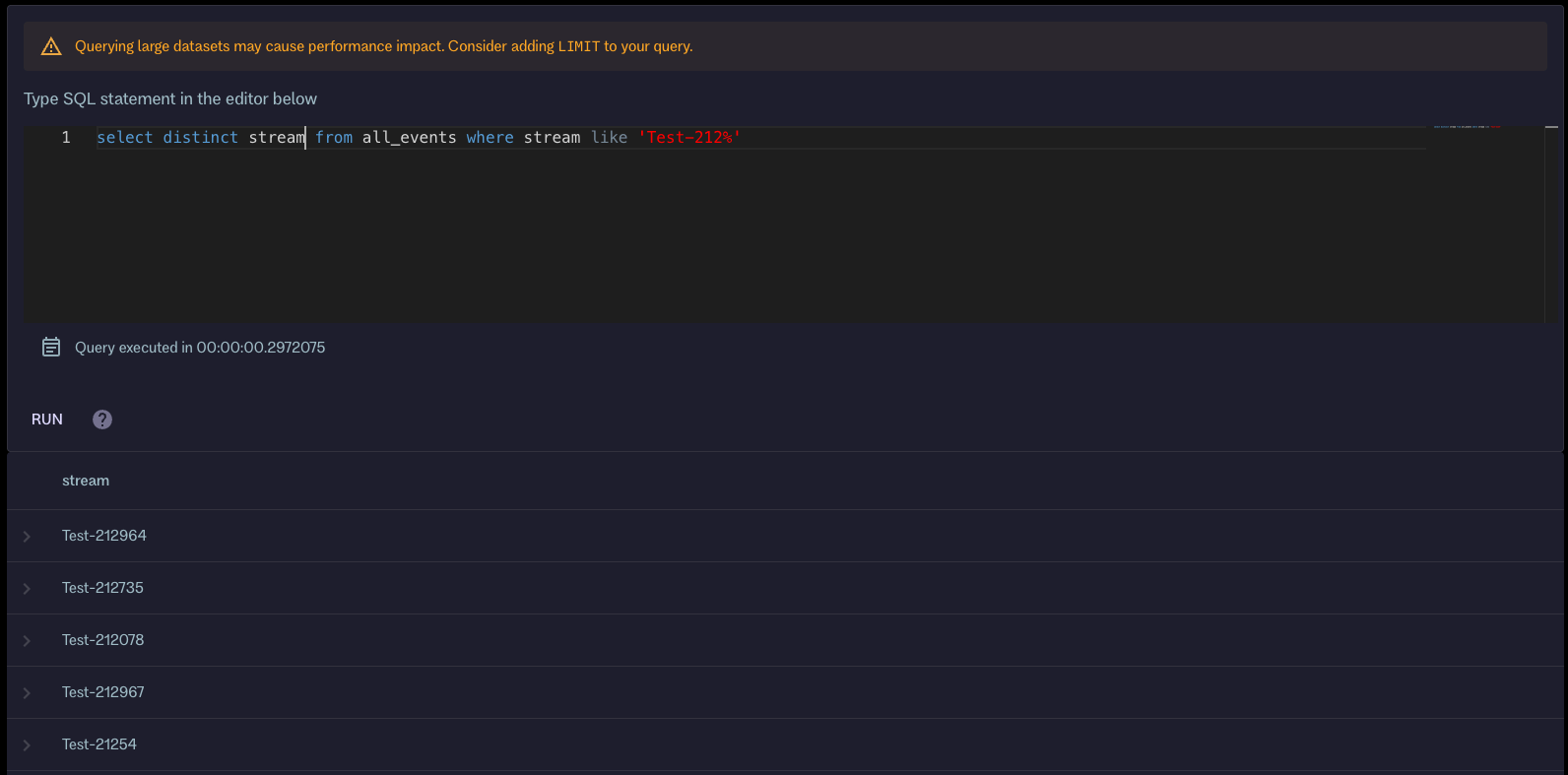
Preview of SQL queries
The new Query page in the embedded web UI allows users to use SQL to query events stored in KurrentDB. The aim of this preview feature is to allow users to explore and analyze their data using familiar SQL syntax without needing to use JavaScript and the projections API for ad hoc queries.
It’s also possible to use SQL queries to find streams based on a stream name mask, count events in streams and across streams, and filter events by event type or category, and to limit queries by event timestamp. Such queries use secondary indexes and run fast. In addition, users can execute queries with predicates on event data and metadata, although such queries may be slower because they require scanning events.
Read more about the feature in the documentation.
OTLP log export
Previous versions of KurrentDB supported exporting metrics to OpenTelemetry-compatible backends. KurrentDB 25.1 extends this support to logs. Since most observability providers support OpenTelemetry, this feature allows users to centralize their logs and metrics in a single backend.
Find out how to configure OTLP log export in the documentation.
Apache Pulsar sink for Connectors
KurrentDB 25.1 introduces a new sink connector for Apache Pulsar, enabling users to stream events from KurrentDB to Pulsar topics. This addition expands the range of supported messaging systems and allows for greater flexibility in integrating KurrentDB with existing data pipelines.
Learn more about the Pulsar sink connector in the documentation.
Other improvements
In addition to the major new features, KurrentDB 25.1 includes several other improvements:
- Ability to run KurrentDB as a Windows Service
- Log record properties (headers)
- New metrics for monitoring projections and persistent subscriptions
- Server garbage collection optimizations
- New default for StreamInfoCache size
- Various bug fixes and performance improvements in the Connectors and Archive features
Learn more about these improvements in the release notes.
